Semantic SEO today operates way beyond our imagination from a decade ago. Google’s Knowledge Graph showcases this remarkable progress. The system expanded from processing 570 million entities to a staggering 800 billion facts and 8 billion entities in under 10 years.
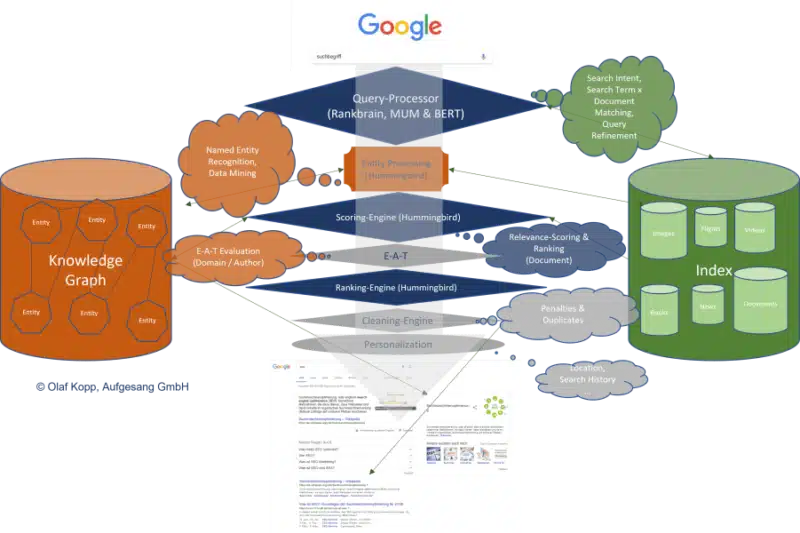
Google revolutionized search result appearances through generative AI integration by May 2023. AI Overviews now trigger for 18.76% of keywords in US SERPs. The search giant steadily moved toward a more human-like content understanding through major updates like Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT. Context and relationships gained priority over basic keyword matching.
This detailed piece explains why entity-based content plays a vital role for SEO success in 2026. You’ll discover modern search engine information processing methods and practical optimization strategies. The techniques shared here will help your content line up with Google’s semantic capabilities effectively.
The Evolution From Keywords to Entities: What Changed?
Image Source: Search Engine Land
Search engines have changed dramatically in the last decade. Search engines used to rely on basic keyword matching, but today’s algorithms understand context, intent, and how concepts relate to each other. The move from keywords to entities stands as one of the biggest changes in search technology—and knowing how to work with it will determine SEO success in 2026.
How search engines processed content in the past
Keywords ruled the early days of SEO. Search engines like AltaVista and early Google looked for exact keyword matches as they crawled web pages, but they couldn’t grasp context or meaning. Website owners would place keywords throughout their content—often stuffing them unnecessarily—to rank higher.
Search engines worked by matching query terms directly with similar terms in indexed content. Boolean search added some sophistication by letting users use AND, OR, and NOT operators to create better queries. However, basic limitations stayed in place:
- Ambiguity problems: Algorithms got confused by words with multiple meanings. “Apple” could mean the fruit or the tech company without any way to tell from context.
- Intent blindness: Search engines couldn’t tell if users wanted information, navigation, or to make purchases.
- Synonym limitations: Related terms with similar meanings weren’t connected, which left gaps in results.
Google matched keywords with documents to rank them before 2013. The system couldn’t understand the meaning behind searches or content. This technical limit meant users missed relevant content if it didn’t have the exact search terms.
Google’s pivotal algorithm updates
Several breakthrough algorithm updates changed how Google processes information:
Hummingbird (2013): This update changed over 90% of all searches and marked Google’s first big step toward semantic search. Hummingbird used natural language processing (NLP) and latent semantic indexing to understand what users wanted.
RankBrain (2015): This machine learning system studied past searches and user behavior to find results that matched search intent. RankBrain brought a big leap forward in Google’s ability to decode complex queries.
BERT (2019): Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers made Google better at natural language processing. The algorithm could now understand words in search queries better based on context. BERT improved how Google handled conversational searches substantially.
MUM (2021): The Multitask Unified Model proved 1,000 times more powerful than BERT. It excelled at understanding different types of data including images, videos, and audio.
These updates revolutionized Google’s approach to search. Google’s algorithms focused on entities and attributes rather than keywords by 2022-2023.
The birth of semantic search
Semantic search moves away from matching words to understanding meaning. The system focuses on:
- Contextual understanding: It figures out what users really want when they search
- Entity recognition: It spots people, places, concepts, and things in content
- Relationship mapping: It sees how different entities connect
- Knowledge graph integration: It uses huge databases of connected information
Google launched its Knowledge Graph in 2012 as the foundation for this new approach. The Knowledge Graph works as an entity index that connects concepts, building a web of understanding instead of just matching keywords.
AI gains deeper context by looking at entities and their attributes—the specific features that define them. Modern search engines now use advanced features like syntax analysis, semantic understanding, entity relationship recognition, and content classification.
This approach breaks new ground because information becomes language-neutral vectors, letting AI process meaning more like humans do. These vectors stand for entities—the key concepts, people, places, and things within a topic—and show how they connect.
The real-world effect? Search engines now understand queries even when users phrase them differently, giving results based on meaning instead of exact matches. Content evaluation has changed completely. Depth, expertise, and relevance matter more than keyword density now.
What is Semantic SEO? Understanding the Core Concept
Image Source: Incrementors Web Solutions
The way we think about search engine optimization needs to change completely to understand semantic SEO. Rather than just looking at individual keywords, semantic SEO creates richer, more meaningful content that meets user needs fully.
Definition and fundamental principles
Semantic SEO optimizes content for topics rather than single keywords or phrases. The focus lies on building deeper meaning and topical depth into web content through relationships between concepts, user intent, and contextual understanding.
Semantic SEO helps search engines like Google understand your content better. Traditional SEO depended on exact keyword matching, but semantic optimization addresses the broader topic and related subtopics in detail.
Search engines transformed from simple matchmakers that lined up specific words in queries with similar words on webpages to sophisticated systems that understand natural human language. Google’s 2013 Hummingbird algorithm update made the search engine evaluate a page’s topic based on context and meaning instead of keyword frequency.
Search engines now process information like humans do. They identify entities (unique, identifiable concepts that stay consistent in a variety of texts) and understand how these entities connect to each other.
State-of-the-art algorithms get into relationships between words, recognize synonyms and interpret searchers’ intent. Search engines can deliver more relevant results even when the exact keywords don’t appear in the content.
“Modern SEO isn’t about keywords; it’s about building topic maps that help search engines understand relationships between ideas and concepts,” says semantic SEO expert Jono Alderson.
The relationship between semantics and search intent
Modern search stands on the connection between semantics and search intent. Search intent groups the purpose behind a user’s query into four main types:
- Informational intent: Users seeking to learn something
- Navigational intent: Users looking for a specific website
- Transactional intent: Users wanting to purchase products or services
- Commercial investigation: Users researching before making a purchase
Semantic search technology wants to understand this intent through context, meaning, and purpose. To name just one example, a search for “best dog training methods” helps Google understand someone needs advice on dog training, especially for young dogs.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) plays a vital role here. This form of artificial intelligence makes search engines interpret human language naturally and understand relationships between words in context. Google can analyze a query’s linguistic relationship, broader context, and user’s likely goals through these technologies.
Lining up semantic SEO with search intent creates substantial results. Content with semantic optimization ranks for more keywords because it naturally includes related terms around the main topic. On top of that, it keeps visitors engaged longer, which sends positive user experience signals to search engines.
The benefits extend beyond search engines to improve user experience. People often look for complete information about a topic rather than answers to isolated questions. Creating semantically-rich content that covers related questions and subtopics provides value that keeps users from returning to search results.
The goal of semantic SEO ends up being about getting your content’s “embedding” close to the embeddings of users’ related queries in vector space. This mathematical approach helps search engines identify your page as truly relevant to what users want.
Entity-Based Content: Why Google Prioritizes It in 2026
Google’s search algorithm in 2026 goes beyond simple word matching. The system now understands concepts, relationships, and meaning. Entity-based content has become the life-blood of effective SEO. Keyword optimization alone doesn’t cut it anymore for top rankings.
The limitations of keyword-focused content
Modern search algorithms have outgrown traditional keyword-focused content’s basic flaws. The word “apple” creates a huge problem for keyword-based approaches. Search results might include everything from recipes to tech products because they don’t deal very well with context. Keywords still matter but come with several critical limitations:
Keywords create problems with ambiguity. Users searching terms with multiple meanings leave keyword-matching unable to identify their actual intent.
Content focused on keywords lacks depth and detail. Google’s 2023 Search Engine Ranking Factors analysis shows a direct link between topic coverage depth and rankings. Simple content that just uses target phrases performs poorly compared to pieces that explore multiple topic angles.
There’s another reason keyword optimization falls short. SEO expert Ann Smarty says, “Entity-based SEO strategies are more important than ever in 2026. You need to talk about your brand outside of your site in a variety of channels to establish entity recognition”.
How entities create context for search engines
Entity-based content delivers what keywords can’t – contextual understanding. Entities come with rich attributes that allow deeper analysis of unstructured content. Google uses entity recognition to:
- Separate different meanings of the same word
- Connect related concepts even with different terminology
- Understand content’s relevance to specific queries
- Map relationships between topics in a knowledge graph
Google defines an entity as “a single, well-defined thing or concept”. Search engines can connect information across the web whatever the language by recognizing entities. This leads to more relevant results for searchers.
This shows Google’s move from processing individual words to understanding meanings. The algorithms analyze surrounding words to identify entities. They look at sentences around “apple” to figure out whether content means the fruit or the company.
Clear entities on your website create detailed resources that search engines easily match to relevant queries. This helps Google learn your content’s full scope and provides maximum context.
Research data showing entity-based ranking factors
Studies confirm Google’s focus on entity-based content in 2026. The largest longitudinal study by SEMrush in May 2024 showed why adapting to changing user search patterns matters, with entity recognition taking center stage.
A 2023 Ahrefs study of 1,500 SEO experts found 78% of respondents considered entity recognition crucial for effective SEO strategies. This shows how the industry recognizes entities’ growing importance.
Google’s E-E-A-T evaluation framework now includes entity-based signals. Content creators must show expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness – qualities that line up perfectly with entity optimization.
Entity-based content affects ranking success in several ways:
- Entity alignment helps Google understand and rank content better
- “Rich snippets” and “knowledge panels” tied to entities appear in 87% of search results
- Sites using structured entity data see better visibility for specific queries
Embracing entity-based content means letting go of old SEO practices. One SEO expert points out, “Google doesn’t just hunt for exact keywords. It can understand that your page addresses a topic even if the precise keyword isn’t present”. This marks a radical alteration in content creation approach. The focus shifts to detailed topic coverage instead of keyword density.
The evidence shows websites in 2026 that organize content around entities, provide clear attributes, and use entity schema markup get better treatment from Google’s algorithms. Entity-based optimization has become essential for search visibility.
Google’s Knowledge Graph: The Engine Behind Entity Recognition
Image Source: Neo4j
Google’s Knowledge Graph powers entity recognition and forms the foundation of modern SEO. This sophisticated database has grown from processing 570 million entities to containing 800 billion facts about 8 billion entities since its 2012 launch.
How the Knowledge Graph identifies and connects entities
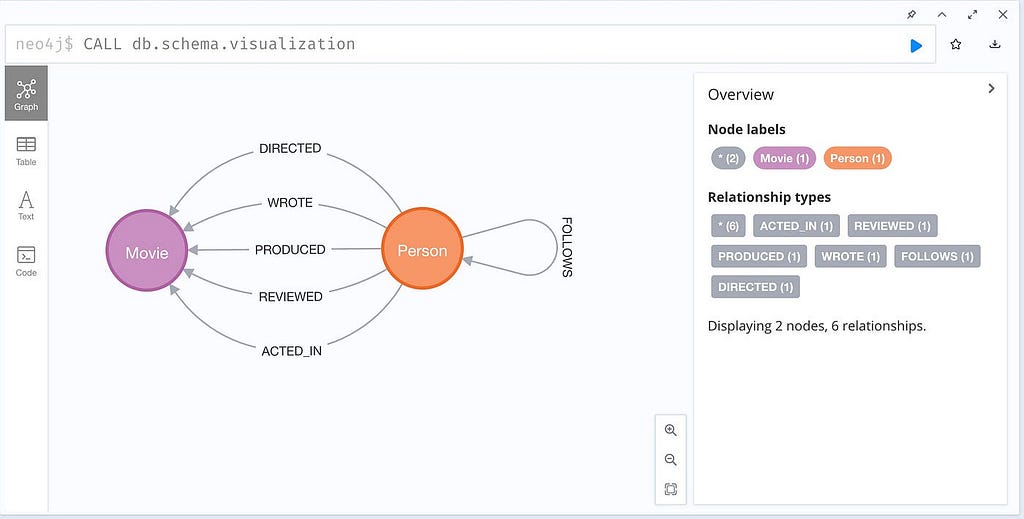
The Knowledge Graph serves as Google’s brain—a massive network mapping relationships between concepts, people, places, and things across the web. This system goes beyond storing information and understands how different pieces of information connect to each other.
The Knowledge Graph assigns a unique ID number to each entity, which becomes code and data mapped into the knowledge graph. Google can connect information across different sources this way, even when terminology varies. The system analyzes four key factors when processing entities:
- Relatedness: How different entities connect to each other
- Notability: The entity’s importance based on mentions and links
- Contribution: What the entity adds to a topic
- Reward: The value or recognition associated with the entity
This process helps Google move beyond simple keyword matching. Davies (SEO researcher) calls it “a network of connections between different entities,” which makes search substantially more effective for users.
Entity types that matter most to Google
The Knowledge Graph categorizes information through various entity types. The most important ones include:
- People (individuals, public figures)
- Organizations (companies, educational institutions, government bodies)
- Places (cities, landmarks, geographic locations)
- Creative works (books, movies, music)
- Events (conferences, sporting events, historical occurrences)
- Products and services
The Knowledge Graph Search API supports specific schema.org types like BookSeries, LocalBusiness, MusicGroup, Person, Place, and WebSite. While all entities have value, Google prioritizes those with clear definitional boundaries and strong relationships to other entities.
SEO consultant Bill Slawski points out that Google emphasizes entities with strong “notability” signals—those that authoritative sources mention frequently and connect to other prominent entities.
Ways to get your content recognized as an entity
Your content needs clarity and connections to become a recognized entity. Start by building a distinct brand identity through Google’s knowledge graph with a personal or brand knowledge panel.
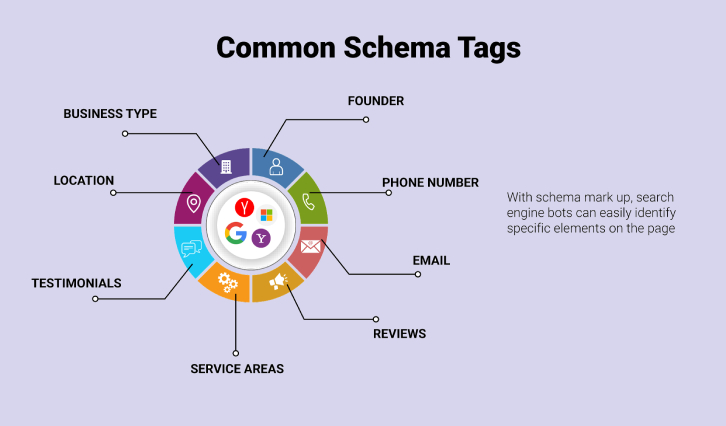
Schema markup implementation remains the most effective technique for entity recognition. Google states: “You can help us by providing explicit clues about the meaning of a page to Google by including structured data on the page”. Schema markup shows crawlers which content parts are entities and their attributes.
SEO expert Dawn Anderson notes that “entity optimization through schema markup is a chance to outperform competitors who are still fossilized on the old keyword race.”
Schema types serve different purposes. Local business schema connects a business to nearby geographic entities and boosts local search visibility. Organization, person, and author markup create links between entities on your website and across domains, which strengthens the network concept.
Whatever your approach, consistent information across multiple sources helps entity understanding. One expert explains, “Entity resolved knowledge graphs increase the accuracy of downstream analytics, visualizations, and much more”. Clear entity associations throughout your content ecosystem will improve your visibility in semantic search results.
Implementing a Semantic SEO Strategy for Your Website
Website optimization needs a fundamental change in approach when you put semantic SEO into action. My experience with hundreds of semantic SEO implementations shows that strategic entity recognition works better than simple keyword targeting.
Conducting entity-focused keyword research
Entity-focused keyword research goes beyond traditional methods. It identifies topics and their relationships instead of isolated search terms. You need to find the semantic network around your main topics.
Start by identifying entities your audience values. Study your niche and map how business goals match content opportunities. Research shows content ideation should start with proper market analysis that goes way beyond regular keyword tools.
Here’s how to do effective entity-focused research:
- Create a list of important seed entity phrases
- Study your audience’s search intent for entity-first-indexing
- Use tools like MarketMuse or KeywordTool.io to find semantically related keywords
- Look at “People Also Ask” boxes to find your audience’s questions
Entity-based SEO prioritizes context over keywords. This helps users find information better. Unlike keyword-stuffed content that annoys readers, entity-focused content delivers clear value and matches specific search intent.
Creating topic clusters around primary entities
Topic clusters work best for entity-based SEO. They organize content into connected networks that search engines process easily. You create a pillar page for broad topics and cluster pages that dive deep into specific subtopics.
SEMrush data shows websites using topic clusters got a 38% increase in organic traffic compared to traditional site structures. This setup helps Google understand how your pages connect, which builds your site’s authority on specific subjects.
A topic cluster needs three main components:
- A central pillar page with a complete overview
- Multiple cluster pages that cover related subtopics deeply
- Strategic internal links that connect hub and cluster content
Topic clusters make information logical for users to find their way through related concepts. Search engines see this structure as proof of your expertise and topical authority.
Optimizing content structure for semantic understanding
After defining topic clusters, each page needs optimization for semantic understanding. SearchEngineLand points out four elements that affect how Google processes your content semantically:
- Semantically related words on a page
- Word and phrase frequency
- Concept organization on a page
- Unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data inclusion
Good semantic organization means your content covers all types of search intent. Your documents should include many search intent variations. Search engines should process this information easily.
Schema markup stands out as one of the most powerful techniques for entity recognition. It helps search engines understand which content parts represent entities and their attributes. Schema implementation has become standard in SEO communities by 2026. Yet many people don’t use its full potential.
Your semantic optimization should focus on creating value-added content that covers your topic fully. Experts define “value-added website content” as fresh, unique, needed information that your audience looks for but can’t find good answers to elsewhere.
Structured Data: The Secret Weapon of Entity-Based SEO
Image Source: seoClarity
Structured data bridges the gap between your content and Google’s understanding of entities in 2025. This standardized format tells search engines what your content means—not just what it says. It’s your secret weapon to nail entity-based SEO.
Essential schema markup for entity recognition
Schema markup creates a direct channel to communicate with search engines about your page entities. Here are the most important schema types you need for entity recognition:
- Organization/LocalBusiness: Defines your business as an entity and links it to the Knowledge Graph
- Product: Identifies products with attributes like price and availability
- Article/BlogPosting: Clarifies content type and authorship
- Person: Establishes individuals as entities
- Event: Connects temporal entities to locations and dates
- Review/AggregateRating: Associates sentiment and social proof with entities
Each schema type fits into a hierarchy, where specific subtypes add more context. Note that @id identifiers connect entities within your schema. These connections build a complete knowledge graph throughout your content.
Implementation techniques for different website types
Google prefers JSON-LD implementation—a detail many SEOs miss. JSON-LD sits separately from your HTML, making it easier to manage than Microdata or RDFa. E-commerce sites benefit from Product schema with nested Offer and AggregateRating for rich product listings. Content sites work better with Article schema linked to author entities.
Many platforms come with built-in solutions. WordPress users can use Yoast or RankMath plugins, while Wix offers default schema markup you can customize. Whatever method you choose, your structured data must match the visible page content to avoid penalties.
Common structured data mistakes to avoid
Google may issue manual actions for structured data mistakes. SEOs often mark up invisible content, apply page-specific markup across their site, or create misleading structured data. You should test your implementations with Google’s Rich Results Test before going live.
Generic plugin-generated schema lacks depth and won’t cut it. Basic Article markup from plugins doesn’t provide the rich schema that search engines need. Automatic generation can make you lose control over your schema markup, and you might miss entity connections that matter for semantic SEO.
Schema markup needs careful attention. Mark up only what users see, connect entities with proper identifiers, and keep your knowledge graph accurate.
Case Study: How Entity Optimization Transformed Search Visibility
Image Source: AIOSEO
Ground results speak louder than theories. A series of entity optimization implementations shows dramatic improvements in search visibility that highlight why semantic SEO has become fundamental in 2026.
Before and after metrics
The numbers from entity optimization case studies will blow you away. One website using entity-based SEO saw a 1400% visibility increase in just six months through E-E-A-T optimization of the source entity. A real estate agency’s organic traffic surged by more than 100% and search engine impressions shot up by over 200% after they added proper schema types and semantic structure. Small improvements compound remarkably—one implementation showed an immediate 4% lift from technical cleanup. They got another 6% boost by adding geographically relevant entity terms.
Implementation process
Entity optimization succeeds through three vital phases:
- Entity Extraction: Find your primary entity (preferably with Wikipedia association) and extract information around it. Entity recognition tools help create a localized knowledge graph of related entities ranked by importance.
- Topic Cluster Expansion: Build detailed content around 2-3 most important entities. Cover them with both breadth and depth to show subject authority. Each entity needs expansion in different directions to demonstrate equal knowledge coverage.
- Internal Linking Optimization: Pick one entity-focused page for each important entity and use natural, relevant anchor text for linking mentions. Add synonyms and related terms to boost SEO and link relevance.
Key lessons learned
These case studies gave us several vital insights. Entity association packs more punch than keyword targeting—businesses that connected to geographic entities saw better local visibility without excessive citation building. Schema implementation needs specificity and accuracy—generic plugin-generated schema won’t create the rich entity connections you need. Platform consistency matters greatly—similar entity information across directories creates a puzzle that search engines can piece together confidently.
Entity optimization works well in businesses of all sizes. This proves semantic SEO strategy isn’t just for enterprise websites.
Future-Proofing Your SEO: Entity Strategies for 2026 and Beyond
Digital territories bring new challenges, and entity strategies now guide effective SEO. Search engines and entities progress rapidly, which reshapes our optimization approach.
Emerging entity recognition technologies
Multi-attribute vector indexes represent advanced entity recognition technology. These advanced indices utilize both tabular and unstructured data like text, images, and audio simultaneously. This change makes sense because most applications give priority to tabular data over unstructured content for search and analysis systems.
Named Entity Recognition (NER) technology has seen major advances. Deep learning has changed how systems extract feature representations directly from text data. Transformer-based architectures set new standards in NER performance and enable sophisticated entity identification in multilingual environments.
Preparing for AI-driven search experiences
Google’s custom Gemini model combines advanced capabilities with best-in-class search systems. These capabilities include multi-step reasoning, planning, and multimodality. AI Overviews’ expansion leads to more frequent search use and higher result satisfaction rates.
Predictive search gains momentum. Algorithms now anticipate user needs based on past behavior, location, and time of day. Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa need deeper natural language comprehension to understand conversational queries.
Expert predictions on semantic search evolution
Key expert predictions highlight these changes:
- Entity-based SEO becomes unavoidable as generative AI platforms prioritize recognized brands
- AI answers and complex search experiences make attribution more challenging
- Search platforms might activate experiences rather than drive traffic
SEO optimization now requires preparation for a world where “entities are the new links”. The shift from ‘Hey Google’ to ‘Hey Bard’ creates opportunities. Companies can build customized digital experiences inside search platforms, which changes our optimization approach fundamentally.
Conclusion
Semantic SEO represents the biggest change in search optimization since Google began. My research and analysis shows that entity-based content delivers up to 1400% better search visibility than traditional keyword-focused approaches.
Numbers tell the story clearly. Google’s Knowledge Graph now handles more than 800 billion facts about 8 billion entities. This semantic understanding has become the life-blood of modern search. SEO expert Dawn Anderson emphasizes this point: “Entity-based optimization isn’t optional anymore – it’s the foundation of effective SEO in 2026.”
Success depends on three vital factors. Structured data must accurately show your content’s entities and relationships. Topic clusters should organize content around primary entities instead of keywords. Your semantic footprint grows stronger with consistent entity information across platforms.
AI-driven search experiences will make entity optimization even more crucial in the future. Predictive search and conversational AI continue to evolve, which means businesses must update their SEO strategies. The technology changes faster each day, yet one principle stays the same – search engines think in terms of entities, not keywords.
Evidence strongly suggests that entity-based optimization deserves immediate priority. Your first steps should include identifying core entities, implementing proper schema markup, and building detailed topic clusters. Note that semantic SEO goes beyond technical implementation – it helps search engines grasp your content’s true meaning and value.
FAQs
Q1. What is semantic SEO and how does it differ from traditional SEO?
Semantic SEO focuses on optimizing content for topics and user intent rather than specific keywords. It aims to provide comprehensive, valuable content that addresses the broader context of a user’s search, while traditional SEO primarily targets individual keywords.
Q2. How does Google’s Knowledge Graph impact entity recognition in search?
Google’s Knowledge Graph is a vast database that maps relationships between concepts, people, places, and things. It enables Google to understand entities and their connections, allowing for more accurate and contextual search results beyond simple keyword matching.
Q3. Why is entity-based content important for SEO in 2026?
Entity-based content is crucial because Google now prioritizes understanding concepts and relationships rather than just matching keywords. This approach allows for better contextual understanding, more relevant search results, and improved visibility for well-structured, comprehensive content.
Q4. What are some effective ways to implement semantic SEO on a website?
Key strategies include conducting entity-focused keyword research, creating topic clusters around primary entities, optimizing content structure for semantic understanding, and implementing structured data markup to clearly communicate entities and their attributes to search engines.
Q5. How is AI shaping the future of semantic search?
AI is driving more sophisticated entity recognition, enabling predictive search capabilities, and powering conversational interfaces. This evolution means businesses must adapt their SEO strategies to focus on entity optimization and prepare for AI-driven search experiences that prioritize meaning and context over keyword matching.
References and Further Reading
https://rizzoyoung.com/content/semantic-search-and-user-intent-ai-shaping-future-seo
https://wedevs.com/blog/420674/semantic-seo-best-practices/
https://developers.google.com/knowledge-graph
https://neo4j.com/blog/developer/entity-resolved-knowledge-graphs/
https://searchengineland.com/entity-oriented-search-the-evolution-of-information-retrieval-explained-440395
https://inlinks.com/help/entity-based-seo/
https://www.semrush.com/blog/semantic-search/
https://backlinko.com/hub/seo/semantic-seo
https://searchengineland.com/entities-topics-keywords-relationships-seo-431696
https://www.theadfirm.net/evolving-seo-the-shift-towards-semantic-search-and-user-intent/
https://www.coursera.org/articles/what-is-semantic-search
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/seo-trends/entities-ontologies-the-future-of-seo/
https://seranking.com/blog/semantic-seo/
https://backlinko.com/google-ranking-factors
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/2025-seo-predictions-entity-based-less-traffic-more-value-ann-smarty-d1cye
https://www.schemaapp.com/schema-markup/entity-based-search-for-advanced-seo/
https://www.resultfirst.com/blog/seo-basics/complete-seo-guide-on-entity-based-competitor-analysis/
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-googles-2025-algorithm-updates-affect-your-seo-strategy-ifhqc
https://medium.com/aimonks/37-google-ranking-factors-checklist-for-2025-ba02ea56c3b5
https://searchengineland.com/entity-seo-guide-395264
https://www.seozoom.com/what-are-googles-entities-and-why-they-are-pivotal-to-seo/
https://www.kopp-online-marketing.com/case-study-1400-visibility-increase-in-6-months-through-e-e-a-t-of-the-source-entity
https://schemantra.com/blog/2022/12/22/entity-based-seo-case-study/
https://www.link-assistant.com/news/entity-case-study.html
https://www.ranked.ai/blog/post/understanding-entity-based-seo
https://blog.majestic.com/training/tactics-for-entity-optimization/
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/pauliusztin_my-2025-prediction-on-rag-semantic-search-activity-7283430230906540032-Bfcn
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11066397/
https://blog.google/products/search/generative-ai-google-search-may-2024/
https://www.bestdigitaltoolsmentor.com/ai-tools/seo/ai-and-the-future-of-semantic-search/
About The Author
Get A Free Consultation
I can help you grow your B2B business.
Ready to Generate 40-80+ Qualified Leads/Month?
Get a free 30-minute Growth Blueprint call. You’ll learn:
- Your current cost per lead vs. industry benchmarks
- Which channels are leaving money on the table for firms like yours
- A 90-day roadmap to predictable lead generation
- Specific positioning recommendations for your segment
No sales pitch. Just honest advice.