A typical B2B lead interacts with your company 5 to 50 times before making a purchase decision.
Prospective clients connect with your brand through countless touchpoints. They download content, attend webinars, read email campaigns and engage with social media posts. Each account’s experience can include dozens or hundreds of touchpoints.
B2B marketing attribution has become crucial to understand which marketing efforts produce results. Multi-touch attribution models help share credit across interactions and show how different marketing activities contribute to conversions.
The numbers speak for themselves. Companies that match their sales and marketing teams with the buyer’s experience see 2.3 times higher sales conversion rates. Yet the 2024 Gartner CMO Spend Survey reveals only 24% of CMOs believe they have enough budget to execute their strategies.
This piece shows how multi-touch attribution connects marketing interactions to revenue, which helps measure effectiveness and optimize spending. You’ll learn about attribution models, implementation strategies, and solutions to common challenges that will help you understand what works in your B2B marketing ecosystem.
Table of Contents
What is B2B Marketing Attribution?
B2B marketing attribution has become a vital framework that shows which marketing efforts actually drive business results. This analytical approach links marketing activities to revenue generation and provides clarity in today’s complex digital world.
Definition and Purpose
B2B marketing attribution helps identify and assign value to marketing touchpoints that lead to conversions and sales. It creates rules that help marketers learn about interactions that influence buying decisions.
Marketing teams need attribution to track and assess every touchpoint that shapes a prospect’s path to becoming a customer. This approach lets businesses:
- Direct resources to channels that perform well
- Target campaigns based on what appeals to specific audience segments
- Boost lead nurturing efforts throughout the funnel
- Create better synergy between marketing channels
What Does Attribution Mean in B2B Context?
B2B attribution differs from B2C in several ways. It focuses on account-level attribution instead of individual customers. This reflects how B2B purchasing decisions involve multiple stakeholders in one organization.
B2B marketing attribution must handle much longer sales cycles. B2C purchases often happen on impulse, but B2B deals can take weeks, months, or years. These extended timelines create visibility gaps that make it hard to connect early marketing efforts with final conversions.
The collaborative nature of B2B decision-making sets it apart. Different stakeholders from one organization participate with various marketing materials across channels. So tracking and attributing influence over time needs more resilient systems than standard attribution methods.
How Attribution Supports Data-Driven Decisions?
B2B marketing attribution changes decision-making from gut feelings to evidence-based choices. Companies can see which campaigns and channels affect their bottom line directly.
Attribution offers measurable insights that help marketing teams arrange budgets and strategies toward channels that drive revenue and ROI. Teams can justify marketing expenses to leadership by measuring each touchpoint against conversion numbers.
Marketing and sales teams can work together instead of separately. They share insights about influential marketing campaigns and avoid misjudging specific channels. This teamwork creates synergy between departments and arranges all teams toward common business goals.
Why Attribution Matters in Long Sales Cycles?
Long B2B sales cycles make attribution valuable. Sales cycles typically run 6-12 months from first contact to closed deal. Consistent attribution helps connect early marketing efforts with final conversions.
Prospects interact with many touchpoints across channels during these long cycles—both online and ground-level. Marketers might misallocate budgets or fail to nurture prospects well without proper attribution.
Multiple stakeholders in B2B purchasing decisions make it essential to understand each touchpoint’s influence. Decision-makers respond differently to various messages and channels. Marketing teams must track effectiveness across audience segments.
Attribution in long sales cycles helps B2B marketers move from reactive to proactive planning. Teams can spot patterns in customer trips and adjust their efforts to drive better engagement throughout the buying process.
Understanding the B2B Sales Cycle
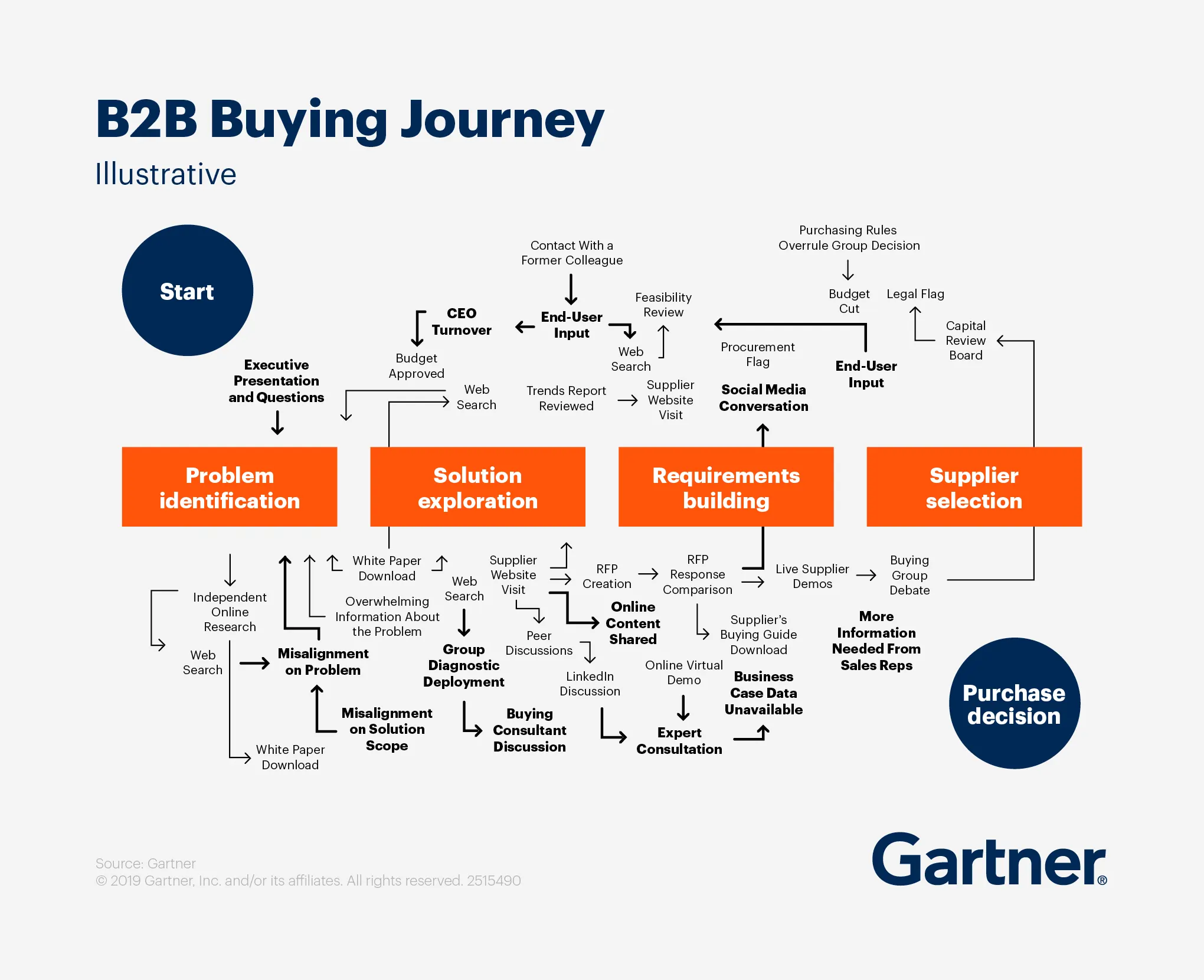
Image Source: Gartner
B2B marketers face unique challenges when they try to track the path from first contact to closing a deal. B2C customers often buy on impulse. B2B sales take much longer because they need multiple people to make decisions.
Why B2b Sales Cycles Are Longer and More Complex?
B2B sales take much longer than B2C sales. Simple products need 1-3 months to close, while complex solutions can take 6+ months. Research from Dreamdata shows B2B customers take about 211 days to make a purchase. A 2024 Dentsu study found it takes around 379 days from research to final deal – that’s 16% longer than in 2021.
Several reasons explain these long timelines. B2B deals cost more money and need approval from many people in the company. These deals also need careful review, detailed negotiations, and plans to put everything in place.
How Multiple Stakeholders Affect Attribution?
B2B buying teams usually have 6.8 different decision makers. Large companies might have 5-11 people involved. These people come from different departments like sales, finance, IT, and leadership. Each person looks at solutions based on what matters to their role.
This makes tracking marketing success harder because each person looks at different content in different places. A CFO wants to know about return on investment, while tech teams care about how to set things up. Marketing that works for one person might not reach another, even though both help make the final choice.
Understanding B2b Customer Journey Stages
B2B customers go through stages: awareness, consideration, conversion, loyalty, and advocacy. But these stages don’t follow a straight line. Gartner found that vendors only talk directly to customers 17% of the time – the other 83% happens through research and internal team discussions.
Identifying Key Touchpoints
Buyers connect with your brand many times during their purchase. A typical B2B customer interacts about 62 times over six months, though this changes based on industry and product type. These touchpoints happen online through websites, downloads, and webinars, as well as offline through calls, meetings, and trade shows.
Account-Based Attribution in Complex Journeys
Old-style lead tracking doesn’t work well for B2B because it misses how buying teams work together. Account-based tracking works better because it shows how marketing and sales activities bring in revenue from entire companies, not just individual leads.
This change from focusing on leads to focusing on accounts means looking at different numbers. Instead of counting qualified leads, teams track how many companies are interested and how much they engage.
First-Touch Attribution
First-touch tracking gives all credit to the first time someone finds your brand. This helps find the best ways to get initial interest but misses how later marketing helps close the deal.
Last-Touch Attribution
Last-touch tracking does the opposite – it gives all credit to the final contact before purchase. This shows what helps close deals but ignores earlier steps that helped make the sale happen.
Linear and Time-Decay Models
Linear tracking splits credit equally among all touchpoints to show the whole customer’s trip. Time-decay tracking gives more credit to recent contacts, assuming they matter more for the final decision.
U-Shaped and W-Shaped Models
U-shaped tracking gives 40% credit each to first and last contacts, with 20% split among middle steps. W-shaped adds another key point (usually when leads qualify) and shares credit between these three main points.
Full-Path and Custom Models
Full-path tracking builds on the W-shape by adding two more steps: creating opportunities and closing deals. Custom tracking lets companies build their own system based on what works for them, using past results and customer behavior.
Multi-Touch Attribution Vs Marketing Mix Modeling
Multi-touch tracking looks at individual customer paths, while marketing mix modeling looks at total results to see how different marketing channels work together. Both methods are great ways to get insights when used as part of a complete measurement plan.
Types of Attribution Models Explained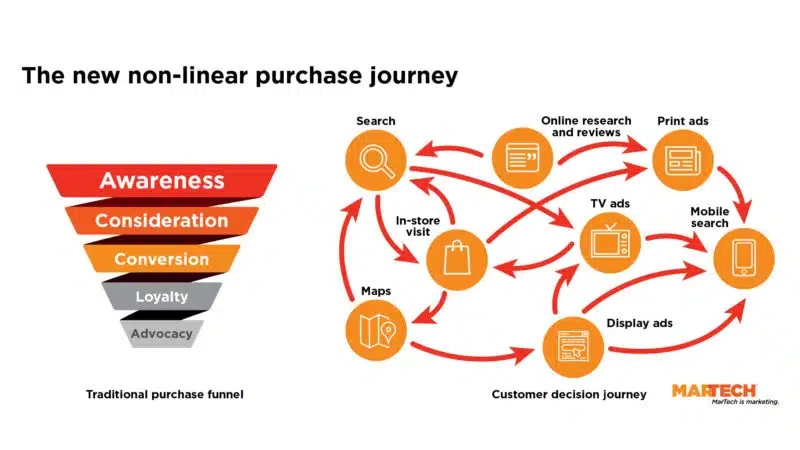
Image Source: MarTech
The right attribution model helps you measure marketing’s effect across your B2B customer’s trip accurately. Research shows customers need 6-8 touchpoints to generate a lead. You need to understand how each model gives credit differently.
One-touch attribution models give all credit to a single interaction. These models are easy to set up at first, but they don’t capture the complexity of B2B buying:
- First-Touch Attribution gives 100% credit to the first interaction. This model helps identify which top-of-funnel marketing channels grab prospect attention effectively. It works best to learn what caught your customer’s eye first.
- Last-Touch Attribution gives all conversion credit to the final touchpoint. Though it simplifies the trip, this approach works well for quick purchases. It shows which channels drive final conversions. The model proves most valuable for products with shorter buying cycles.
Multi-touch attribution models give credit to multiple interactions. They provide a complete view of customer trips:
- Linear Attribution gives equal credit to every touchpoint. Marketers learn which channels help drive conversions consistently. This works best when decisions happen fast.
- Time-Decay Attribution gives more weight to recent touchpoints. It works great for B2B’s longer sales cycles. The model shines when customers interact with touchpoints over long periods. Sales cycles lasting over two months need a longer half-life of 30-45 days.
- Position-Based (U-Shaped) Attribution gives 40% credit to first and last touchpoints. The remaining 20% goes to middle interactions. This balanced approach fits most B2B purchase paths that have clear handoffs between marketing and sales.
- W-Shaped Attribution gives 30% credit each to first touch, lead creation, and last touch before conversion. B2B companies that need leads find this model helpful.
- Full-Path (Z-Shaped) Attribution includes first touch, lead creation, opportunity creation, and customer close touchpoints. Complex sales processes with high customer consideration use this model.
- Custom Attribution lets you set specific weights based on your business needs. This gives the most realistic view but needs deep understanding of customer behavior.
When to Use Each Attribution Model?
Your business goals, sales cycle length, and customer trip complexity determine the best model. Last-touch attribution works for shorter sales cycles and impulse purchases. Products that need research and consideration need multi-touch models.
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) offers a different approach than multi-touch attribution. It analyzes combined data instead of individual trips. MMM shows the big picture with offline channels and external factors. Multi-touch attribution excels at detailed trip analysis. Using both approaches gives the best insights—MMM for planning strategy and multi-touch attribution for improving tactics.
Your model choice should grow with your business. Models that focus on top-of-funnel activities help when awareness drives your goals. Bottom-of-funnel interaction models work better when closing deals matters most. Success comes from matching your attribution approach with your marketing and business goals.
How to Implement Multi-Touch Attribution?
Multi-touch attribution needs careful planning and solid tech foundations. A systematic approach helps capture B2B buyer’s complex trips while providing useful insights.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Your attribution model selection starts with a marketing audit. You should check all channels and touchpoints in your funnel to learn about every interaction. This audit helps you pick a model that matches your business goals.
Your choice should grow with your business goals. Models that highlight top-of-funnel activities work best when awareness matters most. Models focusing on bottom-of-funnel interactions prove more valuable when closing deals becomes the priority. Most companies start with simple first and last-touch features before moving to advanced methods.
These key factors matter when picking your model:
- Sales Cycle Length – Multi-touch models work better for longer cycles
- Channel Diversity – Linear or position-based models suit businesses using multiple channels
- Business Objectives – Your model should match your core marketing goals
Testing different models often gives you the most complete insights. A marketing expert points out, “It’s more a process than a one-time decision, as your attribution model must consistently evolve with your marketing needs”.
Setting Up B2B Conversion Tracking
B2B conversion tracking watches key events showing progress through the sales funnel. Beyond simple pageviews, B2B conversion points usually include:
- Form submissions (requests, quotes)
- Lead generation activities (newsletter subscriptions)
- File downloads (whitepapers, technical specifications)
- Video engagement (product demos, tutorials)
After identifying these conversion points, you can set up tracking systems like device fingerprinting, server-side tracking, or consent-based tracking to link leads with their source channels. Many platforms need JavaScript snippets on your website to track user actions.
Tools for Cross-Channel Marketing Attribution
Effective attribution needs a unified data source that records every marketing touchpoint. This central database prevents data silos and removes differences between multiple sources.
Several specialized tools help solve B2B attribution challenges:
Marketo Measure stands out with its “every-touch attribution” feature that records buyer touchpoints across marketing and sales. This includes first touch, closed deals, and both online and offline interactions. The system automatically collects data from paid media, website interactions, chat, email, webinars, physical events, and direct mail.
Attribution Platform offers user-level tracking throughout customer trips plus account-based marketing attribution. The platform fixes traditional analytics limitations by unifying data transparently and importing cost data automatically from multiple platforms.
Your chosen tool should connect well with other systems. Look for options that work with your CRM, email platforms, social channels, and advertising systems. Smooth integration creates better data flow and makes finding insights easier.
Mapping Customer Journey Touchpoints with Tools
Good mapping creates your attribution model’s foundation. Start by grouping each touchpoint based on how it affects buying behavior. Then use visualization tools to chart the customer’s trip from first contact to conversion.
Interactive dashboards and detailed charts help you see your attribution data and get a complete view of all marketing work. Many platforms show journey details through heatmaps, flow diagrams, and cohort analysis to find where users leave and improve conversion paths.
Tracking Offline and Online Touchpoints
B2B decisions happen both online and offline. You can track offline interactions like trade shows, networking events, or in-person meetings using:
- Call tracking to connect phone talks with digital trips
- QR codes and coupon codes at physical events
- CRM logs to record in-person interactions
Online tracking needs your marketing touchpoints to collect user data efficiently and send it to your central database. Automated alerts can help spot issues like missing data or sync problems between platforms.
Keep testing and improving your attribution approach after setup. One expert suggests: “Keeping it simple initially is best. You can always optimize and improve your attribution model without unnecessarily overcomplicating it right out of the gate”.
Measuring ROI Across the Funnel
ROI measurement turns B2B marketing attribution from theory into a real business advantage. Tracking the right metrics across your sales process helps you learn which marketing investments actually bring in revenue.
Key Metrics to Track (CPL, CAC, MRR, etc.)
B2B attribution needs monitoring of several critical financial metrics:
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) shows how much you spend to get a new customer. You can calculate it by dividing total sales and marketing expenses by the number of new customers acquired. B2B companies measure CAC at an average of $536.
Cost Per Lead (CPL) puts a dollar value on new lead acquisition. The formula is: Total Ad Spend ÷ Total Attributed Leads. B2B CPL measurements range from $65 to $250 in 2025, based on industry and channel.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) shows predictable subscription income and helps track financial health and growth patterns. SaaS companies at the top saw quarterly MRR growth between 85% and 152% from 2022 to 2024.
Return on Marketing Investment (ROMI) shows revenue from marketing versus its cost: (Revenue attributed to marketing – marketing cost) ÷ marketing cost. Marketing investments prove profitable when ROMI goes above 100%.
Lining up Attribution with B2B Sales Funnel
Marketing attribution must connect different touchpoints to proper stages across the B2B funnel. Buyers interact about 36 times before making a purchase. Some trips include hundreds of touchpoints.
Accurate funnel measurement needs tracking of conversion rates between Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) and Sales Qualified Opportunities (SQOs). This helps review lead qualification effectiveness. Pipeline velocity calculations use: (Deals in pipeline × average deal size × win rate) ÷ average sales cycle length.
Connecting Attribution Data to Revenue Outcomes
Closed-loop reporting connects marketing activities to revenue generation. This system tracks the customer’s entire trip from the first touchpoint through conversion. Teams can spot what affects conversions and where prospects drop off.
Marketing-influenced revenue shows the percentage of closed deals that marketing touched at any stage. This metric links marketing efforts to financial results and helps put resources into working strategies.
Reviewing ROI of Marketing Attribution
Attribution effectiveness shows up in lead quality metrics before and after implementation. The CLV:CAC ratio—ideally 3:1 or higher—determines long-term value creation.
Attribution data should let you see:
- The exact relationship between spend, leads, and revenue
- Quantified returns in leads and revenue
- Paths that create leads versus those that generate revenue
Using Attribution Data for Budget Decisions
Attribution insights help make informed budget choices by showing which channels consistently bring profitable outcomes. Good attribution spots specific issues—like Facebook ads with 1:1 ROAS versus Google organic with 50:1 ROAS—and helps shift resources where needed.
Time to revenue matters in budget decisions. This metric shows the duration from first interaction until an account closes as won. It sets realistic expectations for campaign performance timing.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
B2B marketing attribution faces major hurdles despite sophisticated systems. Success depends on tackling these challenges with practical solutions that strengthen your attribution framework.
Data Silos and Fragmented Systems
Most B2B companies work with disconnected data systems that block full visibility into customer experiences. Marketing data sits apart from sales information, which makes tracking attribution almost impossible. These divisions create scattered conversion events and make it hard to spot renewal potential and upselling chances.
To curb fragmentation, build one central hub for customer data. This complete approach helps marketers access, analyze and grasp customer needs across the ecosystem. The result? A shift from brand-focused to performance-driven marketing.
Attribution Window and Tracking Limitations
Wrong attribution windows do more than skew reports – they lead to poor decisions about strategy, spending and performance. Default settings like Google Ads’ 30-day window don’t work for B2B sales that take months or years. This leads to underreported performance.
The solution is simple: Match attribution windows to your actual sales cycle length. Sales cycles lasting beyond two months need longer windows of 30-45 days. On top of that, it helps to use dynamic windows that adjust to real consumer patterns instead of fixed timeframes.
Data Quality Issues and How to Fix Them
About 75% of organizations say at least 10% of their lead data lacks accuracy, remains outdated or breaks compliance rules. Bad data disrupts lead handoffs and reduces sales team efficiency for more than 60% of teams. Plus, 55% can’t properly clean and enrich data with their current tools.
Here’s how to boost data quality:
- Set required contact/account data fields by persona
- Create CRM workflows that connect contacts with deals
- Use server-side tracking to catch data that ad blockers miss
- Include “How did you hear about us?” in forms to understand dark funnel activity
Proving Attribution Accuracy
Causal inference plays a key role in attribution accuracy. We need to think about whether conversions would happen without specific campaigns to verify touchpoint effectiveness. This helps us focus on causes rather than correlations, which grounds insights in reality.
Regular comparison of attribution data across platforms helps verify accuracy. When Meta shows 12 conversions while Google Ads reports 15, we can use Google Analytics 4 as our source of truth.
Cross-Functional Alignment Between Sales and Marketing
The focus shouldn’t be on who gets credit for attribution. Instead, let’s ask questions that drive action: What touchpoint should come next? Where should we invest more? How can we spend smarter?
Top companies see attribution as a business investment that drives revenue, not just a marketing project. Attribution works best as a bridge between teams, connecting scattered data points into a story everyone can follow.
Conclusion
B2B marketing attribution is the life-blood of modern marketing teams who want to measure how campaigns affect complex sales cycles. This piece explores how attribution links different marketing touchpoints to revenue outcomes. It brings clarity to what drives results in long B2B sales processes.
Good attribution strengthens marketers to make data-backed budget decisions. The right multi-touch attribution models help you identify which campaigns, channels, and content pieces influence buying decisions at each funnel stage. Marketing transforms from a cost center to a proven revenue driver with this visibility.
Your specific business needs determine the best attribution model. First-touch models show what drives awareness. Last-touch approaches highlight what triggers conversions. Multi-touch models like linear, position-based, and custom frameworks give detailed views of your customer’s entire trip.
Clean data quality makes attribution work. Even sophisticated attribution models can’t deliver useful insights without unified data flowing between marketing and sales systems. A centralized data repository and team alignment are the foundations of accurate attribution.
Attribution must tie directly to business results. Metrics like CAC, CPL, and marketing-influenced revenue turn attribution from theory into strategic advantage. These financial connections let marketing teams prove their value and optimize spending to maximize results.
Some challenges exist – from data silos to attribution window limits. The benefits are way beyond the implementation hurdles. Companies that become skilled at attribution gain a clear competitive edge. They spend more efficiently, create better-aligned campaigns, and understand what truly drives revenue.
Tomorrow belongs to marketers who use evidence-based attribution. B2B buying cycles grow more complex each day. Your success depends on knowing how to track, measure, and optimize all touchpoints. Start small if needed, but take that first step. This trip toward attribution excellence will reward you with stronger marketing results and clearer ROI than ever before.
FAQs
Q1. What Is B2B Marketing Attribution and Why Is It Important?
B2B marketing attribution is the process of identifying and assigning value to various marketing touchpoints that contribute to conversions and sales. It’s important because it helps businesses understand which marketing efforts drive results, optimize budget allocation, and measure ROI across long and complex B2B sales cycles.
Q2. How Does B2B Attribution Differ from B2C Attribution?
B2B attribution focuses more on account-level attribution rather than individual customers, accounts for longer sales cycles (often spanning months or years), and considers multiple stakeholders involved in the decision-making process. B2C attribution typically deals with shorter, more straightforward customer journeys.
Q3. What Are Some Common B2B Marketing Attribution Models?
Common B2B marketing attribution models include first-touch, last-touch, linear, time-decay, U-shaped, W-shaped, and full-path attribution. Each model distributes credit differently across touchpoints, with some focusing on specific interactions and others providing a more balanced view of the entire customer journey.
Q4. How Can Businesses Implement Multi-Touch Attribution Effectively?
To implement multi-touch attribution effectively, businesses should choose the right model for their needs, set up proper B2B conversion tracking, use specialized attribution tools, map customer journey touchpoints, and track both online and offline interactions. It’s also crucial to align attribution efforts with overall business objectives and continuously refine the approach.
Q5. What Challenges Do Companies Face When Implementing B2b Marketing Attribution?
Common challenges in B2B marketing attribution include data silos and fragmented systems, attribution window limitations, data quality issues, validating attribution accuracy, and achieving cross-functional alignment between sales and marketing teams. Overcoming these challenges requires a unified data approach, proper window settings, data cleansing, and fostering collaboration across departments.
About The Author
Get A Free Consultation
I can help you grow your B2B business.
Ready to Generate 40-80+ Qualified Leads/Month?
Get a free 30-minute Growth Blueprint call. You’ll learn:
- Your current cost per lead vs. industry benchmarks
- Which channels are leaving money on the table for firms like yours
- A 90-day roadmap to predictable lead generation
- Specific positioning recommendations for your segment
No sales pitch. Just honest advice.


